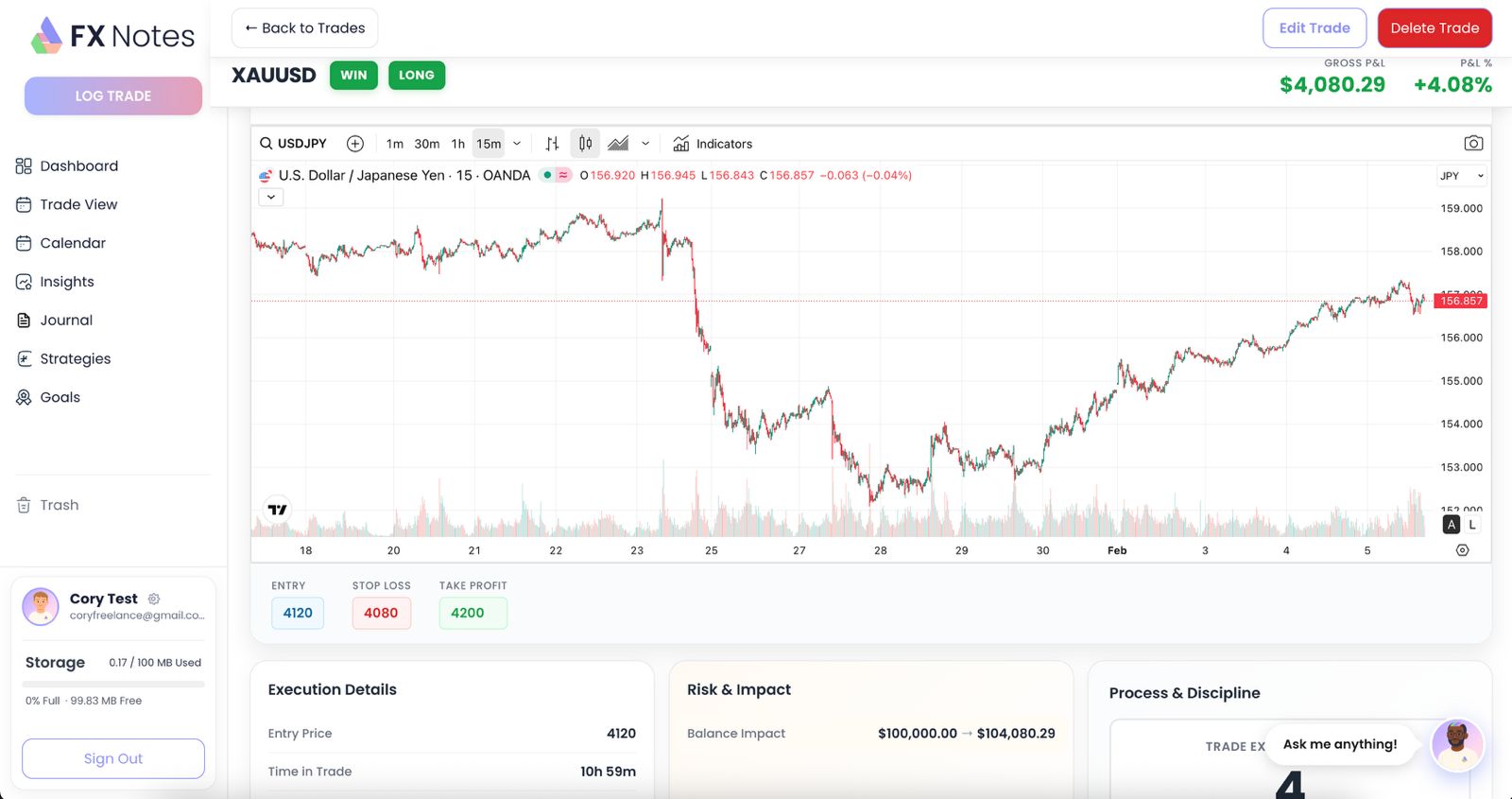
The ability to trade has become one of the most accessible ways to participate in financial markets. With the rise of online trading platforms, anyone with an internet connection can now access thousands of instruments from their phone or laptop.
But while the barriers to entry have dropped, the skills needed to trade successfully have not. Understanding what trading means, how different markets work, and how to manage your risk are essential foundations before you place your first trade.
In this guide, we break down everything you need to know – from the core mechanics of how a trade works, through to the different approaches available, and how tracking every trade with a journal like FX Notes can dramatically improve your results over time.
How Does a Trade Work?
At its simplest, trading work comes down to speculating on whether the price of an asset will rise or fall.
When there are more buyers than sellers, prices tend to go up. When sellers outweigh buyers, prices tend to drop. Every trade you place is a bet on which direction that price will move next.
The Basics of Buying and Selling Financial Assets
Exchanging financial instruments is at the heart of every trade. When you believe an asset will increase in value, you buy it. When you think the price will drop, you sell it.
The difference between your entry price and exit price determines your profit or loss on that trade.
In traditional share ownership, you would buy shares via share dealing through a broker, hold them, and sell later when the value of shares has risen.
But modern financial trading offers many more options. You can speculate on currencies, indices, commodities, and even ETFs – all without ever owning the underlying asset.
The process of transacting in markets varies depending on the instrument and platform you choose, but the fundamental goal is always the same: correctly predicting which direction an asset’s price will move and acting on that prediction.
How Prices Move in Financial Markets
Financial markets are driven by supply and demand. If a company reports strong earnings, more people want to buy its shares, pushing the price up.
If economic data disappoints, participants may sell off positions, driving prices down.
Several factors influence how markets move, including economic reports, central bank decisions, geopolitical events, and overall market sentiment.
Someone who understands these forces is better positioned to identify when to open a position and when to step away.
The key insight for any beginner is that price movements create opportunity. Whether a market is rising or falling, there are potential ways to profit – provided you understand the mechanics and keep risk under control.
Types of Trading
There are several distinct approaches available to retail participants today. Each form of trading comes with its own characteristics, and suitability depends on your experience level, capital, and goals.
Equities
When you trade a company’s shares on the stock market, you are either purchasing stock directly (through a share dealing account) or speculating on the stock price movement through derivatives.
If you believe a company’s stock will rise, you buy shares and profit when the price increases. This approach is popular because companies are tangible – a trader can research their products, earnings, and management before placing a trade.
Many people start with stock market trades before exploring other markets to trade.
The stock market also offers a wide range of opportunities for any trader, from blue-chip companies with steady growth to smaller names that can move sharply in a single session. A stock trade can be as simple as buying shares in a well-known company, or as complex as using derivatives to trade a whole basket of equities.
Forex
Forex is the world’s largest and most liquid market, with trillions exchanged daily. When you trade forex, you speculate on the exchange rate between two currencies – for example, GBP/USD or EUR/JPY.
Forex markets operate 24 hours a day during the working week, giving participants flexibility that equity markets cannot match.
At FX Notes, many of our users trade forex and use our journal to track which currency pairs and sessions produce their best results.
CFD Trading
CFD trading allows you to speculate on price movement without owning the underlying asset. A CFD (Contract for Difference) is a derivative product – you and your broker agree to exchange the difference in price between when a trade is opened and when it is closed.
One of the key advantages of a CFD trade is the ability to go long or short. If you think the price will rise, you go long. If you think it will fall, you go short.
This means a trader can potentially profit in both rising and falling markets.
It is important to understand how spread bets and cfds work before committing real capital. CFDs are leveraged products, meaning you only need to put down a fraction of the full value to open a position.
While this amplifies potential gains, it equally amplifies potential losses. You should always consider whether you understand how cfds work and whether you can afford the risk of losing money.
Spread Betting
Spread betting is a popular approach in the UK, largely because profits from a trade are typically tax-free for most participants (tax laws depend on individual circumstances and may change).
With spread betting, you speculate on the direction of a market by staking an amount per point of movement.
For example, if you believe the FTSE 100 index will rise, you might place a trade at a certain stake per point. If the index rises by 50 points, your profit is your stake multiplied by 50. If it falls, your loss on that trade is calculated in the same way.
Spread betting and CFD approaches share many similarities as both allow you to take a position on price movements without owning the underlying asset. Many platforms let you choose between using spread bets or cfds depending on your preference and location.
Index Participation
An index tracks the performance of a group of shares from a particular market or sector. Popular indices include the FTSE 100, S&P 500, and DAX 40.
When you trade an index, you speculate on the overall direction of that group rather than any single company.
This is a useful way to gain exposure to an entire market in a single trade. Rather than trying to pick individual equities, you can take a view on whether the broader market will rise or fall – making it appealing for those who prefer to follow macroeconomic trends.
ETFs
ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) are another way to access a basket of assets in a single transaction.
They can track an index, a commodity, a sector, or a specific investment strategy, and function on exchanges just like individual equities, making them straightforward to access throughout the day.
Derivative Trading
Derivative products encompass any instrument that derives its value from an underlying asset. This includes CFDs, spread betting, options, and futures.
Derivatives are widely used by retail participants because they offer leverage, the ability to trade in both directions, and access to markets for you to speculate on that might otherwise be difficult to reach directly.
Key Concepts Every Trader Should Know
Before you get into trading with real money, there are several concepts that every trader should understand.
These form the foundation of successful performance and will help you build your confidence across any market. Whether you are a new trader or have been placing trades for years, revisiting these fundamentals is always worthwhile.
Short Positions
Managing Risk
Chart Analysis
Long and Short Positions
When you go long on a trade, you are betting that the price will rise. Going long simply means buying an asset with the expectation that its value will increase.
Going short is the opposite – you speculate that the price will fall. In derivative markets, this is just as straightforward as going long. You sell first and aim to buy back at a lower price.
The ability to profit whether markets rise or fall is one of the main advantages of derivative products over traditional share ownership. It means you can potentially benefit regardless of direction, provided your prediction is correct.
Managing Your Risk
Every trade carries the possibility of loss, and without proper controls, a single bad trade can wipe out weeks of gains.
Effective risk management involves setting stop-losses on every trade, never risking more than a small percentage of your account on any single position, and understanding the relationship between reward and risk before you enter.
At FX Notes, our journal helps you track your risk metrics for every trade automatically, so you can see at a glance whether you are staying within your own rules.
Chart-Based Analysis
Technical analysis is the study of price charts and patterns to predict future market movements. Those who use it look at historical price data, support and resistance levels, moving averages, and other indicators to identify setups.
While not everyone relies on charts, this approach remains one of the most widely used in the world of trading. Many successful participants combine chart-based analysis with fundamental research and sound risk controls.
Understanding Market Swings
Volatility refers to how much and how quickly the price of an asset moves. Highly volatile conditions can present significant trading opportunities, but they also carry greater risk.
One market might move 5% in a single day, while another barely shifts at all. This volatility is what creates both opportunity and danger.
Understanding these dynamics helps you size your positions appropriately, set realistic profit targets, and avoid being caught out by sudden swings.
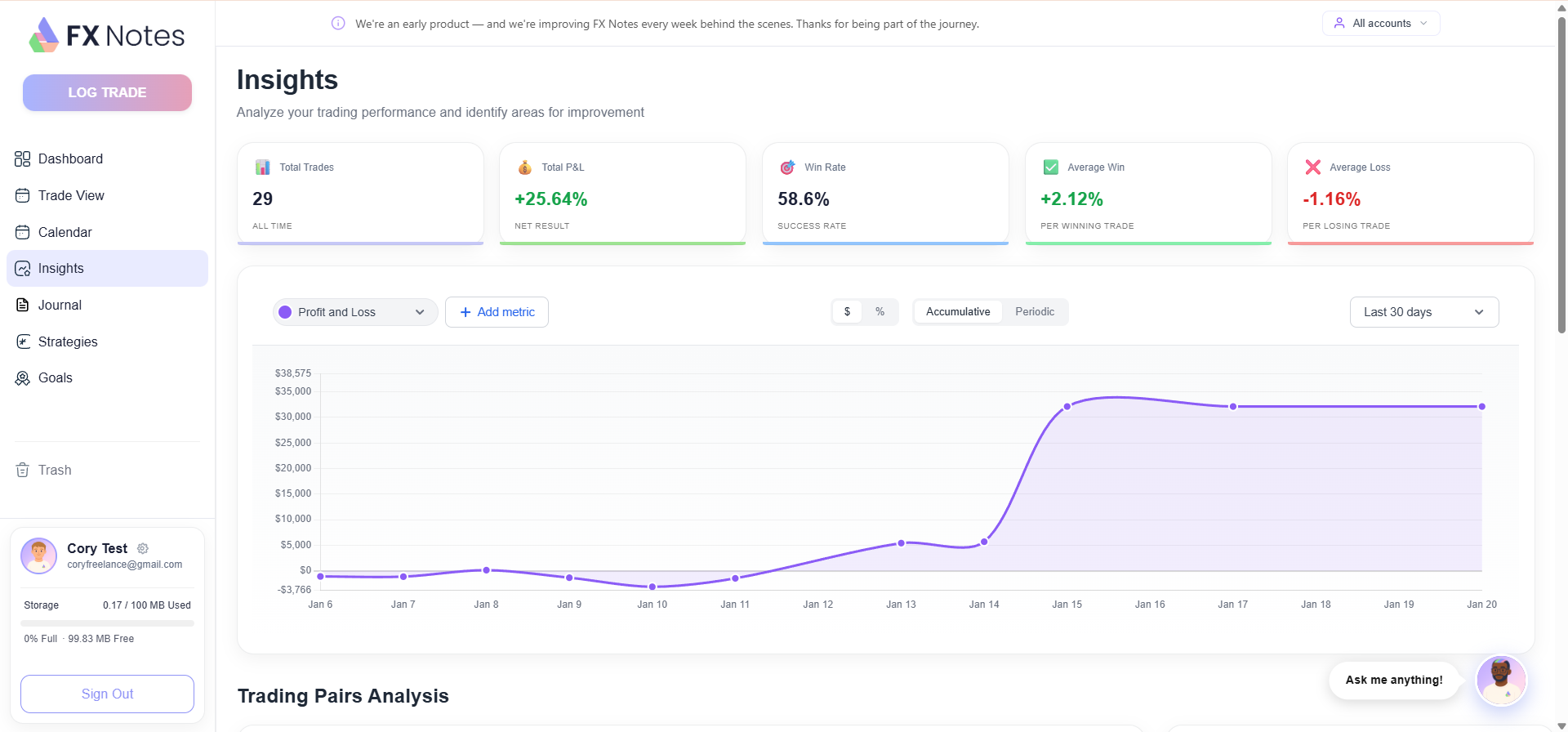
Choosing a Trading Platform and Getting Started
Choosing the right trading platform is one of the most important decisions you will make.
Your platform is where you will execute each trade, manage open positions, analyse charts, and monitor your profit and loss.
A good platform should offer access to the markets you want, competitive spreads, reliable execution, and useful charting tools.
Some well-known providers include IG UK. IG Trading and Investments Ltd is authorised and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority, giving participants confidence in the security of their funds.
IG services include spread betting, CFD access, and share dealing across thousands of markets. Resources like IG Academy can also help you learn to trade through structured courses and educational content.
When evaluating any platform, consider the range of markets available, the quality of the charting tools, the speed of execution, and the level of help and support offered. Some platforms also provide features specific to particular regions, so always check availability in your country or jurisdiction.
Using a Demo Account
Most reputable brokers offer a demo account that lets you practise with virtual funds. This is invaluable for testing your approach, getting comfortable with a new platform, and understanding how different markets behave – all without putting real money at risk.
We always recommend that anyone new spend time practising before moving to live markets. Use a demo account to experiment with different instruments and develop your confidence in reading charts and placing orders.
Opening a Live Account
Once you feel ready, the next step is to open a live account with your chosen broker. The process typically involves providing identification, completing a suitability questionnaire, and depositing funds.
When you are ready to start trading, begin small. Focus on one or two markets, keep your position sizes conservative, and track every single trade.
This is where FX Notes becomes essential – our AI-powered journal records each trade automatically, giving you the data you need to review what is working and what is not.
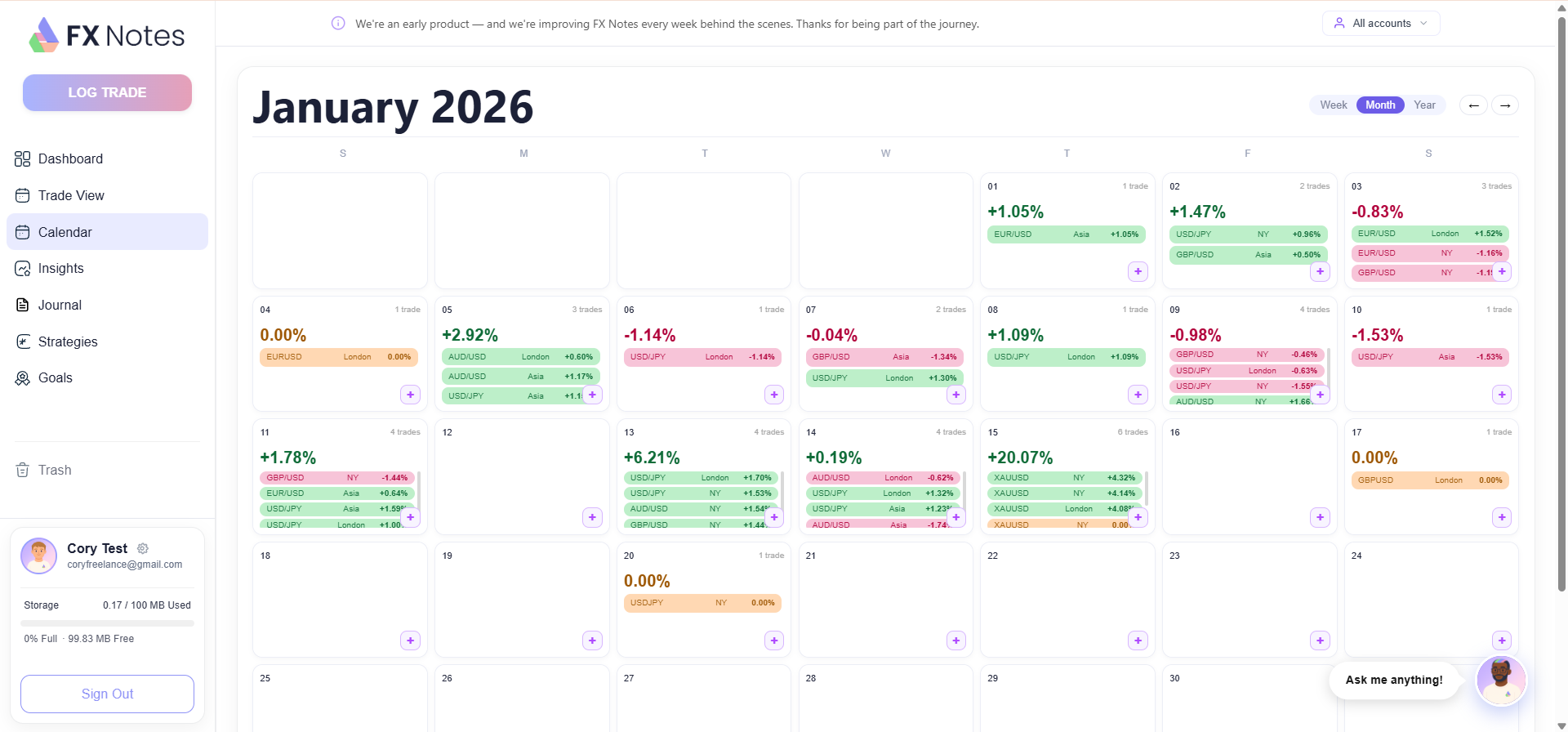
Trading and Investing: What Is the Difference?
Trading and investing are often confused, but they represent different approaches to financial markets.
Investing typically involves buying and holding assets for the long term – years or even decades – with the goal of building wealth gradually through appreciation and dividends.
By contrast, those who trade focus on shorter-term price movements. A trade might be held for seconds, minutes, hours, or days. The goal is making a profit from relatively small price fluctuations, often using leverage to amplify returns on each trade.
Neither approach is inherently better. Many people do both – investing a portion of their capital for long-term growth while actively placing shorter-term trades with another portion.
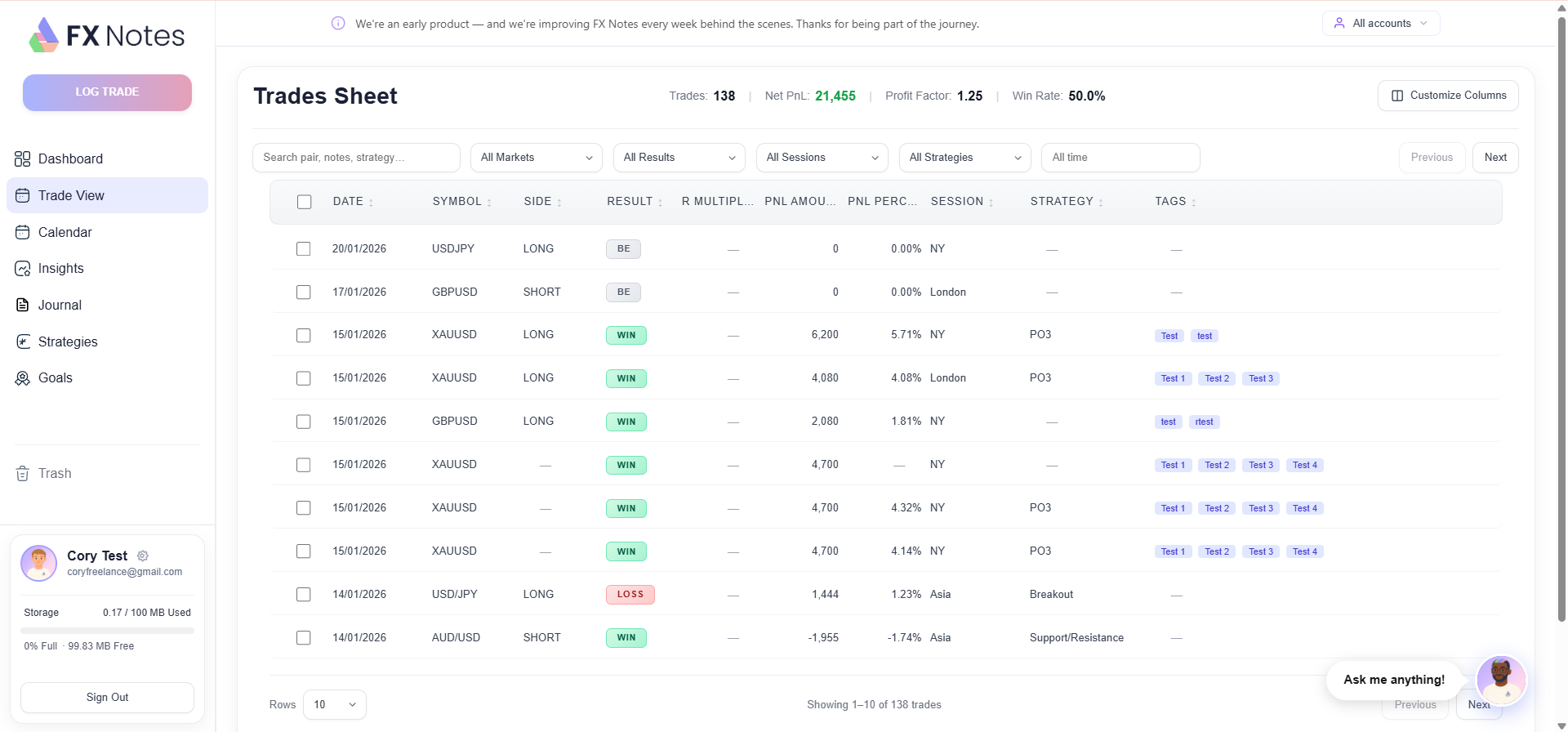
How to Improve: The Importance of a Journal
The single most effective thing any trader can do to improve is to keep a detailed journal.
Every professional trader reviews their trade history to identify patterns, eliminate mistakes, and refine their approach. Without this kind of review, a trader is essentially repeating the same errors without ever realising it.
A good journal should capture your entry and exit points, your reasoning for each trade, your emotional state, and the outcome.
Over time, this data reveals exactly what is driving your results, which setups produce winning trades, and where you need to improve.
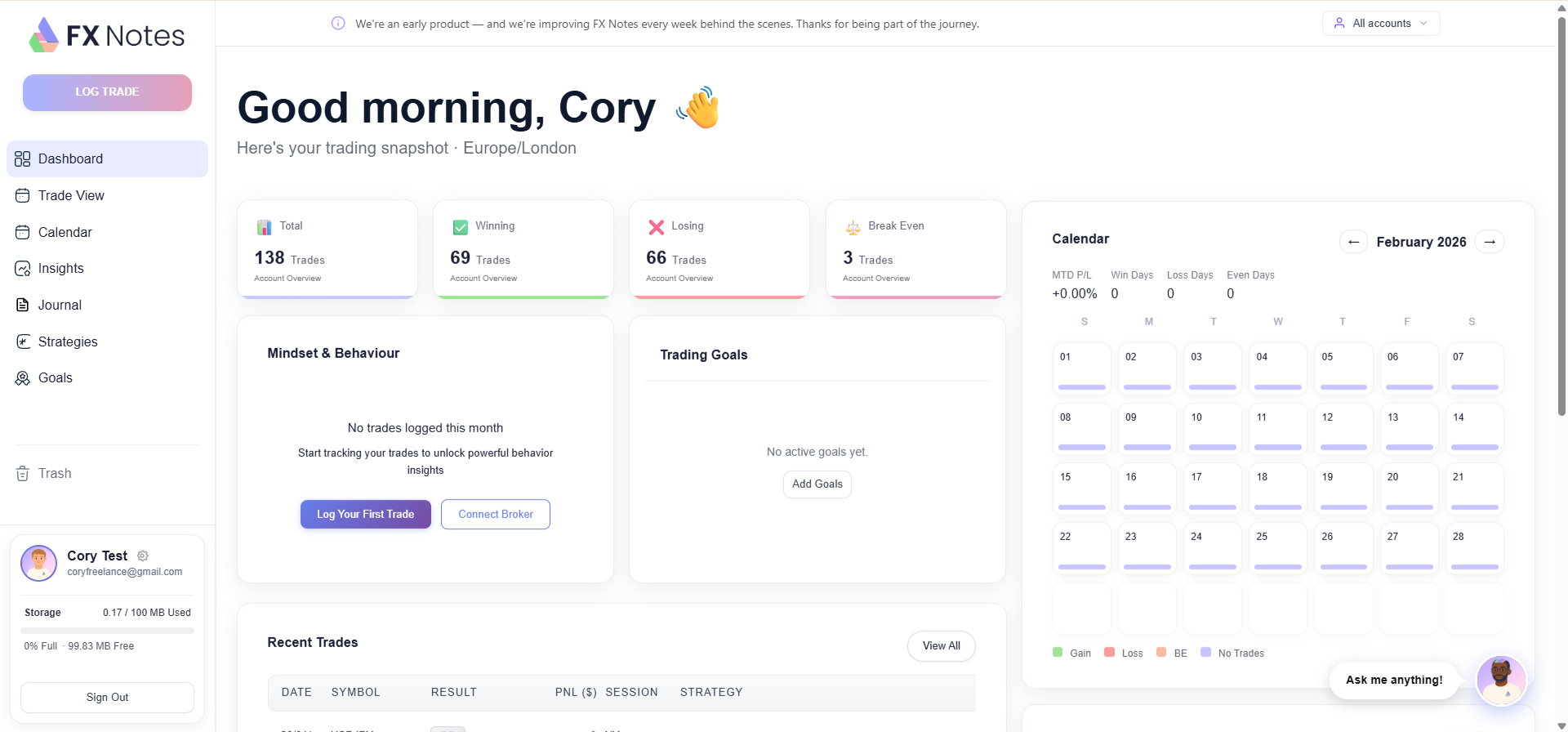
Trading with FX Notes
At FX Notes, we have built our AI-powered journal to make this process effortless. With a single click, you can record, review, and improve your trade performance.
Our platform auto-records each trade and organises them by date, asset, and strategy – so you spend less time on admin and more time actually getting better.
Whether you are a beginner just finding your feet or a trader with years of experience, trading with us gives you the tools to identify your edge and trade with greater consistency.
Our journal captures the decisions, mindset, and behaviour patterns that truly shape trade results – because in our experience, those who review their trades are the ones who improve.
Benefits and Risks of Trading
Every trade carries both potential reward and potential risk.
On the positive side, you have the opportunity to profit from price movements across thousands of markets, the flexibility to trade from anywhere, and the ability to take a position on both rising and falling prices – the price will rise or fall, and either direction can present a trade opportunity.
However, the risks are equally real. Leveraged products like CFDs and spread betting mean you can lose more than your initial deposit on a trade. Markets can move against you quickly, and heightened conditions can amplify losses just as easily as they amplify gains.
Key ways to protect yourself include using stop-losses on every trade, keeping position sizes appropriate, never placing a trade with money you cannot afford to lose, and continuously reviewing your trade performance to ensure you are on track.
Regulation
If you are based in the UK, your broker should be regulated by the relevant authority such as the FCA. This provides important protections including the segregation of client funds and access to the Financial Services Compensation Scheme.
Always verify that any platform or broker you use is properly regulated before depositing funds. Regulation does not guarantee profits, but it does provide a safety net and ensures the broker operates to a certain standard.
Trading for Beginners: A Simple Roadmap
If you are new to this, here is a straightforward path to help you get started.
Keep Learning, Keep Improving
There is always more to discover. From understanding how spread bets and cfds work to refining your trading strategies, the journey toward consistent profitability is ongoing. Every trade you take is an opportunity to learn.
At FX Notes, we are here to support that journey. Our journal is designed to help you sharpen your decision-making and take control of your trade performance – one trade at a time.
Whether you prefer equities, currencies, indices, or derivatives, the principle is the same: track every trade you do, learn from the data, and keep improving. That is what separates the traders who succeed from those who do not.


